
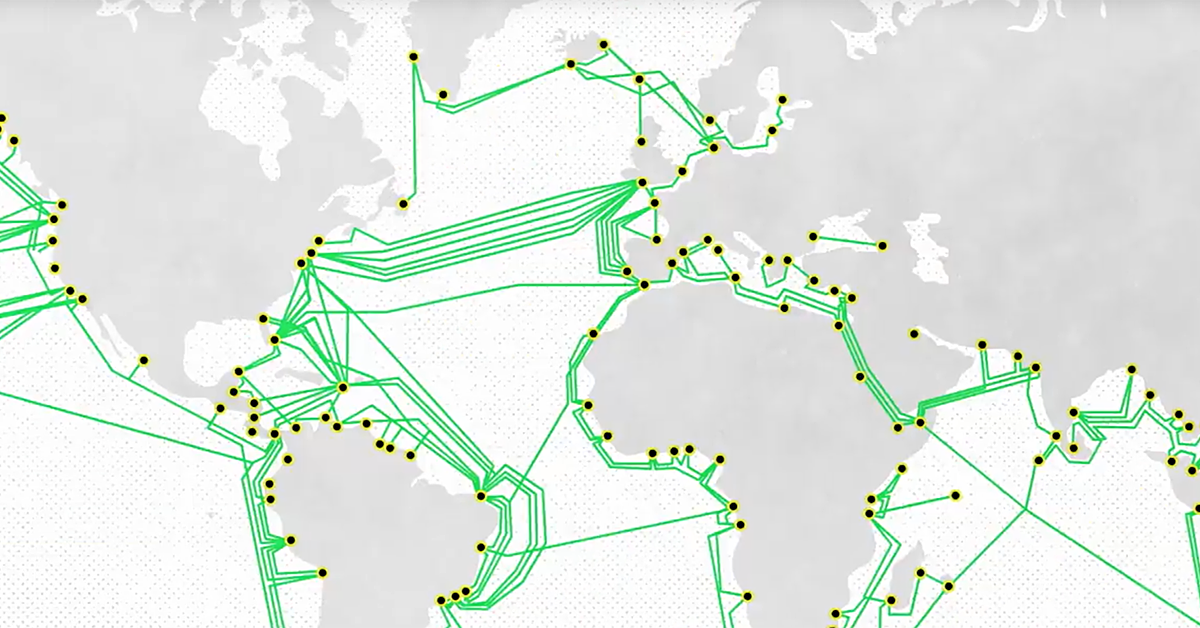
The second-most connected part of world is the UK – which pioneered the laying of submarine cables in the second half of the 19th century. They said the most-connected country in the world is the United States, with cable landing points on both coasts that connect it to most other continents. “Today, an entire network of fibre-optic cables connects almost every corner of the world, enabling the hyper-connected world that many of us take for granted.” GCN owns and operates a national backbone comprised of more than 3100 km of fiber-optic lines. Researchers wrote: “Submarine telecommunications have come a long way since 1842, when Samuel Morse sent the first submarine telegraph transmission under the waters of New York harbour. Tier 1 Internet providers are the networks that are the backbone of the Internet. ISPs are classified into a 3-tier model that categorizes them based on the type of Internet services they provide. It was created by the Oxford Internet Institute, which used data on the routes of all fibre-optic cables to make a simplified abstract map. ISPs provide transport of Internet traffic on behalf of other ISPs, companies or other non-ISP organizations, and individuals.

The overview of the world’s submarine fibre-optic network was created to show how information traverses the world. The backbone market is highly competitive. In Michigan, rough terrain, including forests and dense. The backbone consists of long-distance networks mostly on fiber optic cables that carry data between data centers and consumers.
#Internet backbone map free
A London Underground-style map of the cables that form the backbone of the internet has been created by Oxford academics. Connectivity, even via wireless networks, requires access to a backbone fiber-optic network. Internet Exchange Map TeleGeography’s free interactive Internet Exchange Map depicts over 300 active Internet exchanges and more than 500 buildings in which those exchanges reside.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
